Post Preview
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Casters
- Types of Casters
- Materials Used in Caster Wheels
- Applications of Casters
- Factors to Consider When Choosing Casters
- Maintenance and Safety Tips
- Innovations in Caster Technology
- Conclusion
Introduction to Casters
Casters are crucial components found across countless pieces of equipment and furniture, enabling effortless mobility and improving efficiency in everyday tasks. Typically constructed with a wheel and a mounting assembly, casters allow objects to glide smoothly across surfaces. Learning about the different types, materials, and uses of casters ensures you select the best option for your application. For those seeking high-quality brands, Albion casters are a reputable solution with a wide product range to meet diverse needs.
Selecting the right caster goes beyond choosing the right wheel—it’s about matching specific features to the task, optimizing movement, and extending product longevity. Whether you need support for heavy-duty machinery or a smooth, quiet roll for hospital beds, understanding caster fundamentals will help you make an informed decision.
Types of Casters
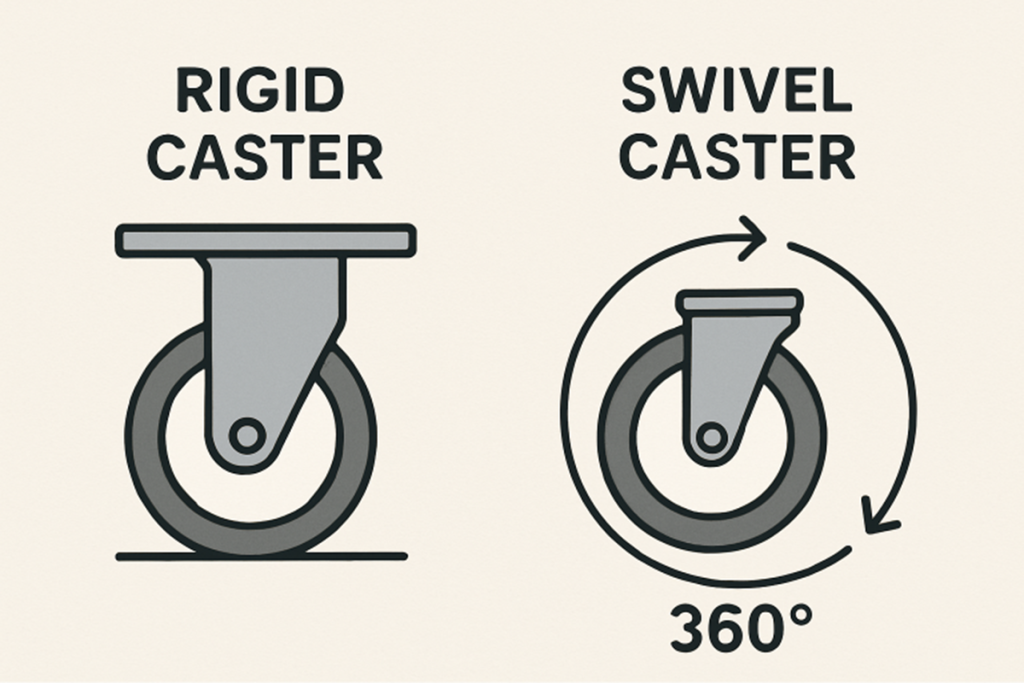
While casters may look similar, they serve different functions depending on their construction. The two basic categories are:
- Rigid Casters: Designed for straight-line movement, rigid casters offer stability, making them ideal for equipment that rarely changes direction.
- Swivel Casters: With a 360-degree swivel joint, these casters excel at maneuverability, facilitating easy turns and navigation in confined spaces.
Industries often use a combination of both, installing rigid casters at one end and swivel casters at the other, which provides a balance between stable motion and agile steering.
Materials Used in Caster Wheels
The choice of caster wheel material affects performance, noise levels, and longevity, and Wood Magazine offers helpful guidance on different rolling models to consider. The most common materials include:
- Rubber: Soft and shock-absorbing, rubber casters minimize noise and leave no marks, making them the first choice for indoor use.
- Polyurethane: Known for its resilience against chemicals, abrasion, and wear, polyurethane is often used in warehouses and manufacturing plants.
- Nylon: Lightweight and cost-effective, nylon wheels are perfect for lighter loads and smooth indoor surfaces.
- Aluminum: Boasting strong corrosion resistance and durability, aluminum casters are trusted for demanding industrial environments.
- Pneumatic: Featuring air-filled tires, these casters absorb shocks and deliver outstanding performance over uneven or rough terrain.
- Cast Iron: Built for extreme durability and heat resistance, cast iron excels in harsh, high-temperature environments such as foundries.
Applications of Casters
The adaptability of casters is reflected by their use across a wide array of sectors. Here are a few leading industries and their main applications:
- Healthcare: Hospital beds, medical devices, and supply carts leverage casters for near-silent operation and smooth handling, which is vital for patient comfort and hygiene.
- Manufacturing: Heavy-duty casters allow factories to move machinery, tools, and inventory efficiently, reducing manual handling and risk of injury.
- Retail and Office: From shopping carts and display fixtures to ergonomic office chairs, casters make rearrangement simple and streamline movement for staff and customers alike.
- Food Processing: Casters in these environments are often stainless steel and high-temperature resistant, conforming to strict hygiene controls and withstanding rigorous cleaning requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Casters
Choosing the right caster involves evaluating several key factors to ensure optimal performance and safety:
- Load Capacity: Assess the total weight the casters must support. Underestimating load requirements leads to premature failure or unsafe conditions.
- Floor Type: The rolling surface shapes your decision. Soft wheels protect delicate flooring, while hard wheels suit carpet or uneven surfaces.
- Environmental Conditions: Exposure to chemicals, moisture, or extreme temperatures dictates the selection of appropriate materials for maximum lifespan.
- Mobility Requirements: Decide between rigid and swivel options, or a combination of the two, to meet your handling needs and workspace constraints.
Maintenance and Safety Tips
Caster performance, longevity, and safe operation hinge on consistent upkeep and mindfulness. Follow these basic maintenance and safety tips:
- Inspect casters routinely for wear, distortion, or corrosion, and replace any compromised parts immediately.
- Remove debris and keep casters clean to prevent jamming and ensure smooth rolling.
- Lubricate swivel bearings and axles according to the manufacturer’s guidance to avoid rust and reduce friction.
- Verify secure and accurate caster attachment, regularly tightening bolts and fittings to help prevent accidents.
Innovations in Caster Technology
Technological progress has introduced several advancements in casters, addressing common challenges and enhancing usability:
- Ergonomic Designs: Reduced push-pull forces make it easier and safer for workers to move heavy loads, thereby lowering the rate of strain injuries.
- Noise Reduction: Advanced wheel materials and bearing technology suppress sound, critical for environments needing quiet operation, such as hospitals and open offices.
- Antimicrobial Coatings: Increasingly vital in healthcare and food sectors, these coatings help maintain sanitary conditions by inhibiting bacterial growth on caster surfaces.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types, materials, and application areas for casters is foundational for selecting the right product. Attention to load capacity, floor compatibility, and environmental exposure ensures reliability and longevity. With ongoing advances in ergonomic and antimicrobial design, the humble caster continues to evolve, supporting safer and more productive workplaces and living spaces. Periodic maintenance and attentive selection help casters deliver optimal performance—an essential, often overlooked element of efficient operations across industries.
